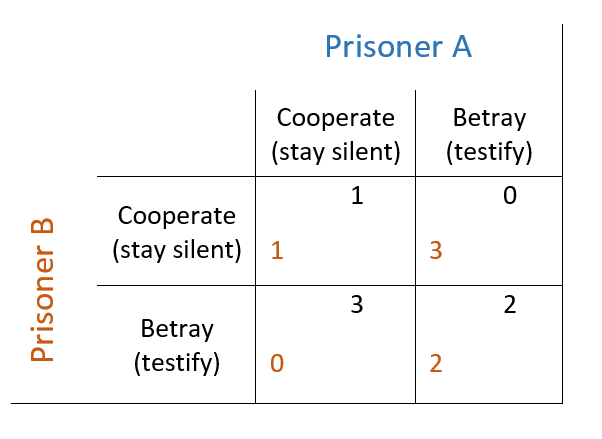
The application of the prisoners’ dilemma to international systems.
Question
Apply the prisoners’ dilemma and apply it to a contemporary international system.
Answer
The prisoners’ dilemma is a representation of ‘game theory’, which is a concept that recognises the way that actions of entities can interact in order to determine outcomes.
The above diagram represents the dilemma, where the numbers represent years of jail time. Cooperation produces the best overall outcome, but both individuals stand to benefit by breaking this deal, as long as the other does not. If both break the deal then a moderate outcome is achieved for both.
Thus the game represents the strategies and incentives that affect entities participating within a system.
If we consider the global political and economic environment we can see how the game can be applied through international trade. Mutual free trade can benefit importing countries through the increase of supply of a scarce good, leading to lower equilibrium prices and a higher level of demand satisfaction. Where this is reciprocal both countries may benefit from better supply of goods and from export earnings.
Imposition of tariffs, perhaps due to political disagreement or concern over balance of trade, increases the effective price of imported goods. This leads to less being imported from the country the tariff is placed on, reducing their export revenue. Meanwhile, the country that placed the tariff gains revenue from the tariff payments.
Mutual tariffs cause this effect for both countries so overall trade is reduced, but this is counterbalanced by tariff income – the overall benefit is less than mutual free trade.
A political example can be seen in a Cold War style situation. Where two countries can either be friendly ensuring security at low cost, or can develop military capability to destroy the other. The development of such capability is costly, but the political benefit of having the capability when your opponent does not is significant. If both have the capability they have some security, but at a high cost and with no advantage over their rival.